A sensitive, accurate and standardized method for MRD detection and monitoring
The clonoSEQ® Assay is a robust, highly-validated tool for identifying and monitoring measurable residual disease (MRD) in lymphoid malignancies.[1] Across a variety of large, multi-center clinical trials, clonoSEQ has generated a wealth of peer-reviewed clinical evidence in disease states including multiple myeloma (MM), B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), and chronic lymphocyticleukemia (CLL).[2,3]
Review specific data for:
Multiple Myeloma
Data Spotlight
COLLABORATORS
Maria-Victoria Mateos, University of Salamanca, Salamanca, Spain
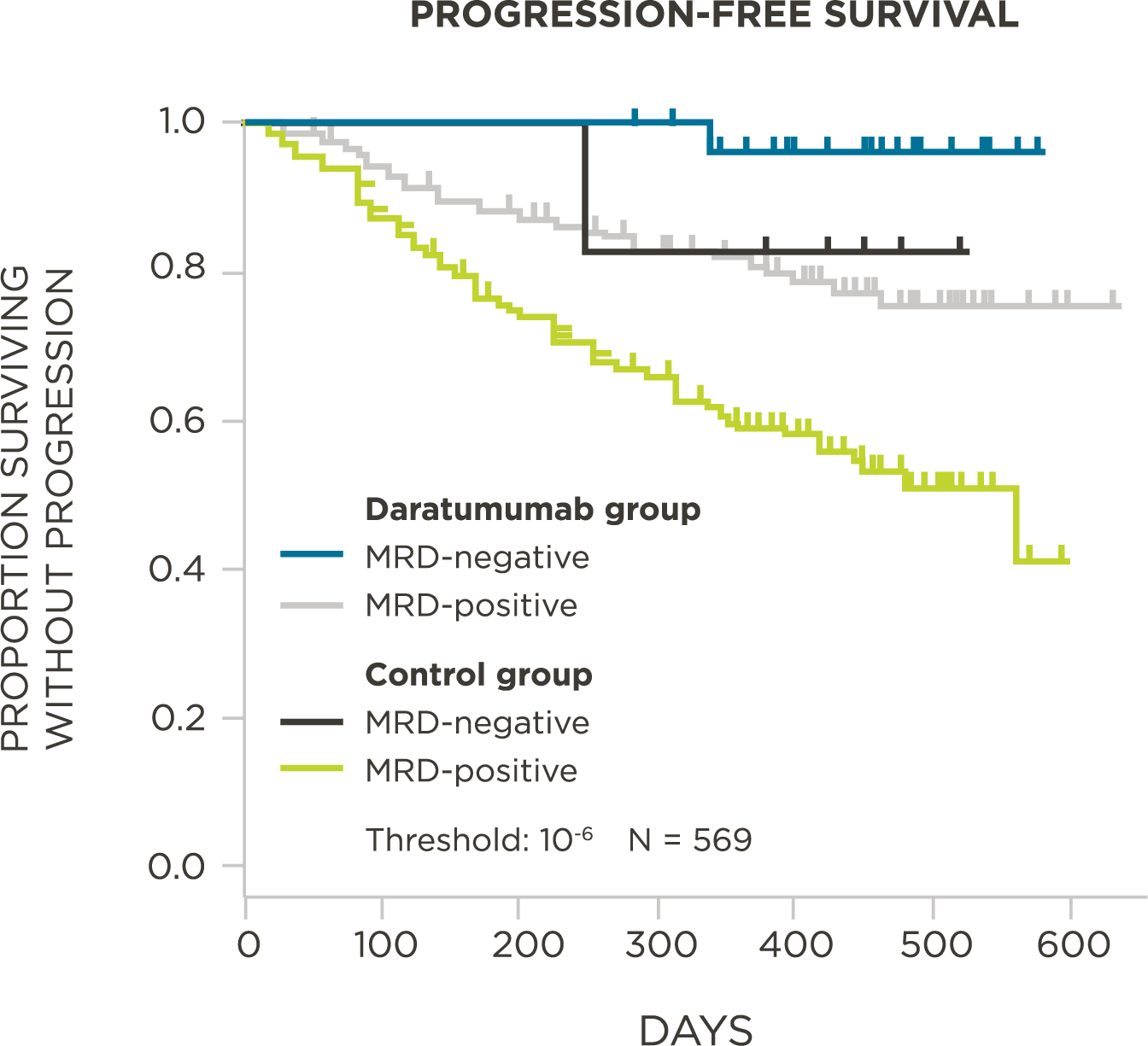
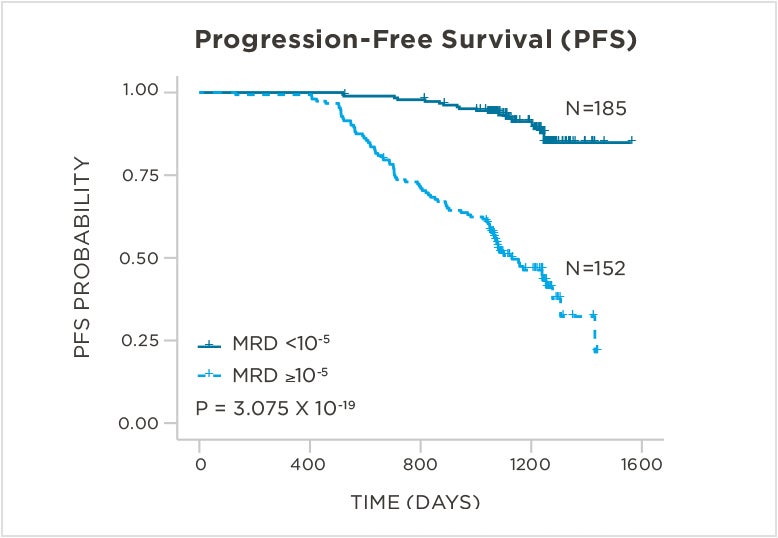
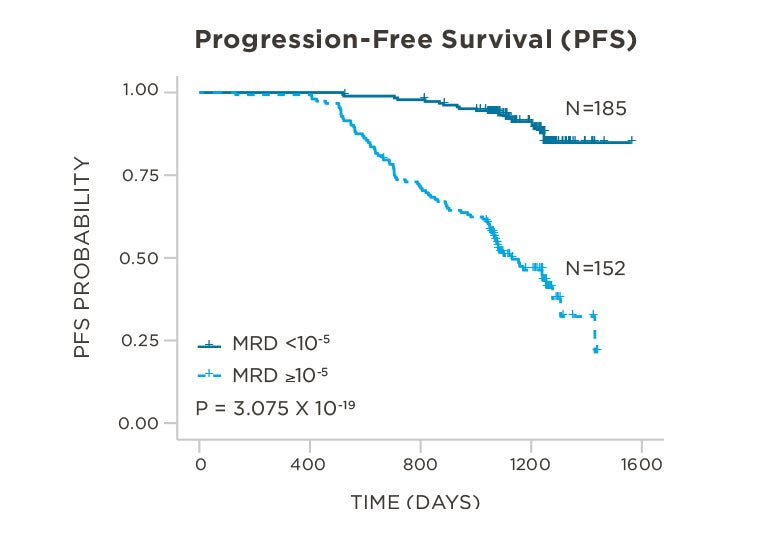
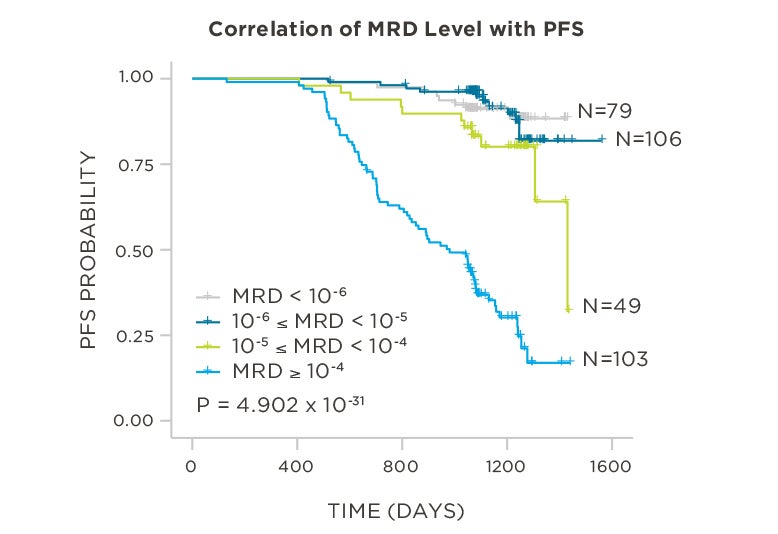
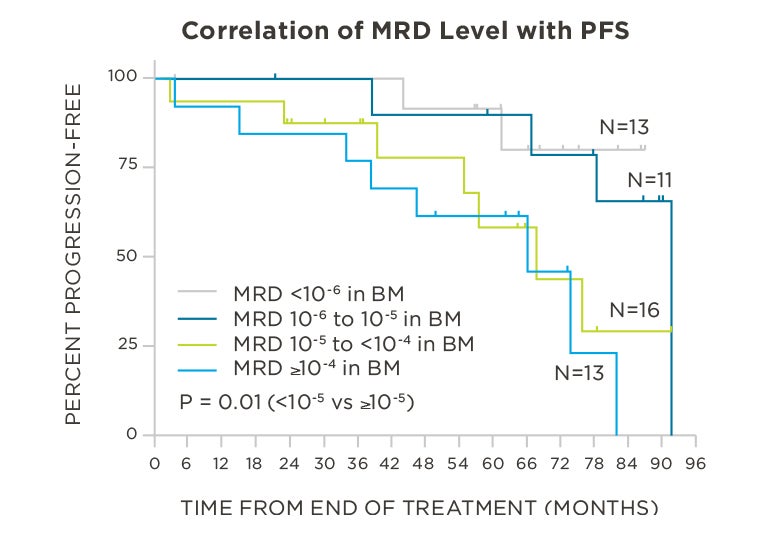
PATIENTS
569 relapsed and refractory patients assessed for MRD by clonoSEQ at the time of suspected complete response (CR)
STUDY OBJECTIVE
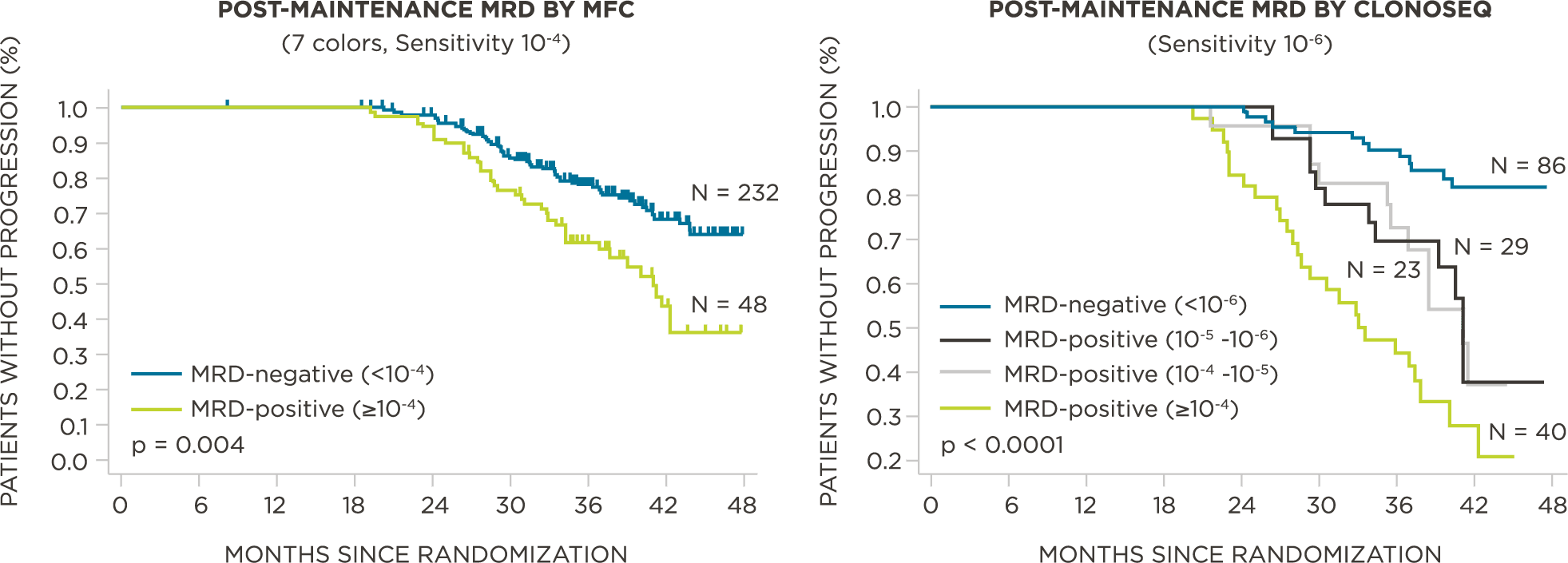
Evaluate use of clonoSEQ MRD testing for prognostic evaluation by correlating MRD results to PFS.[4]
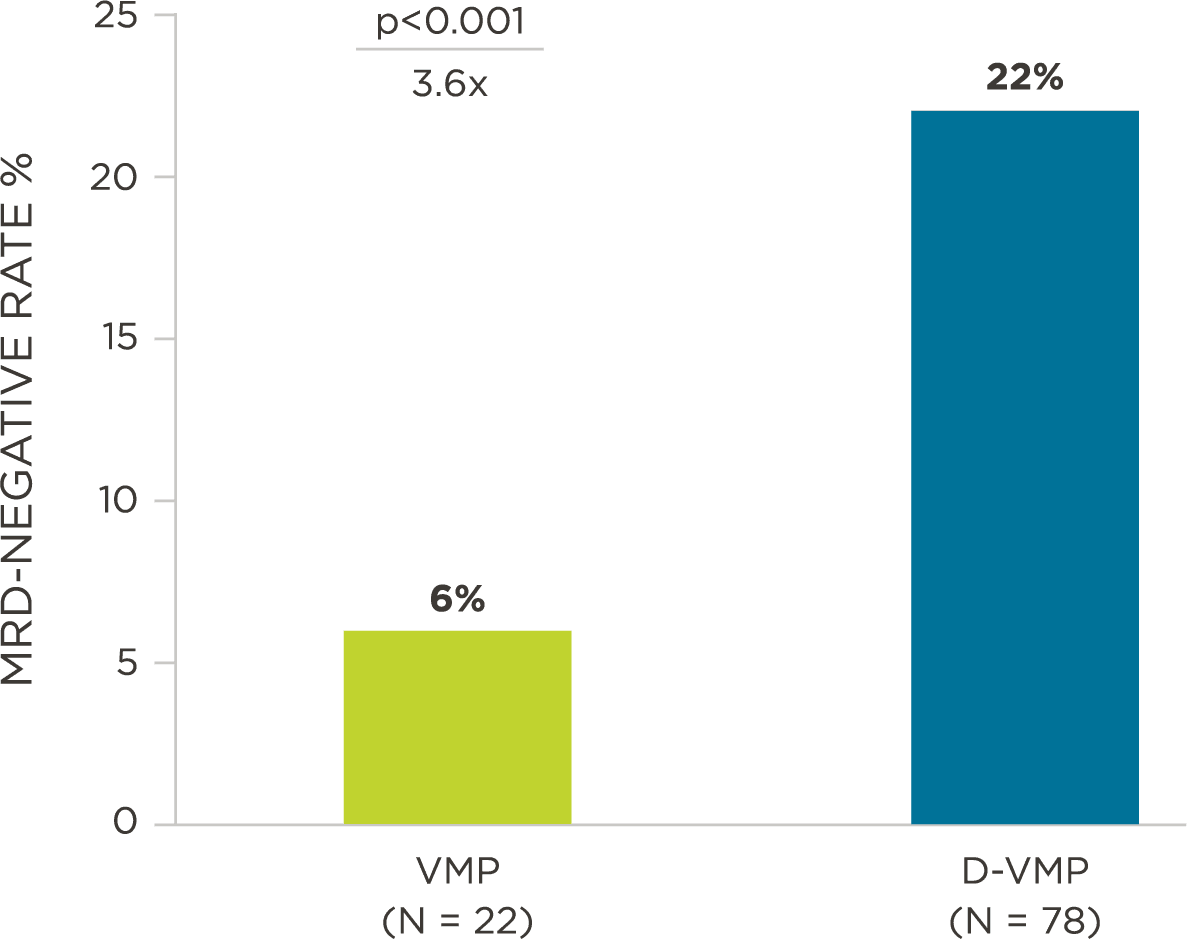
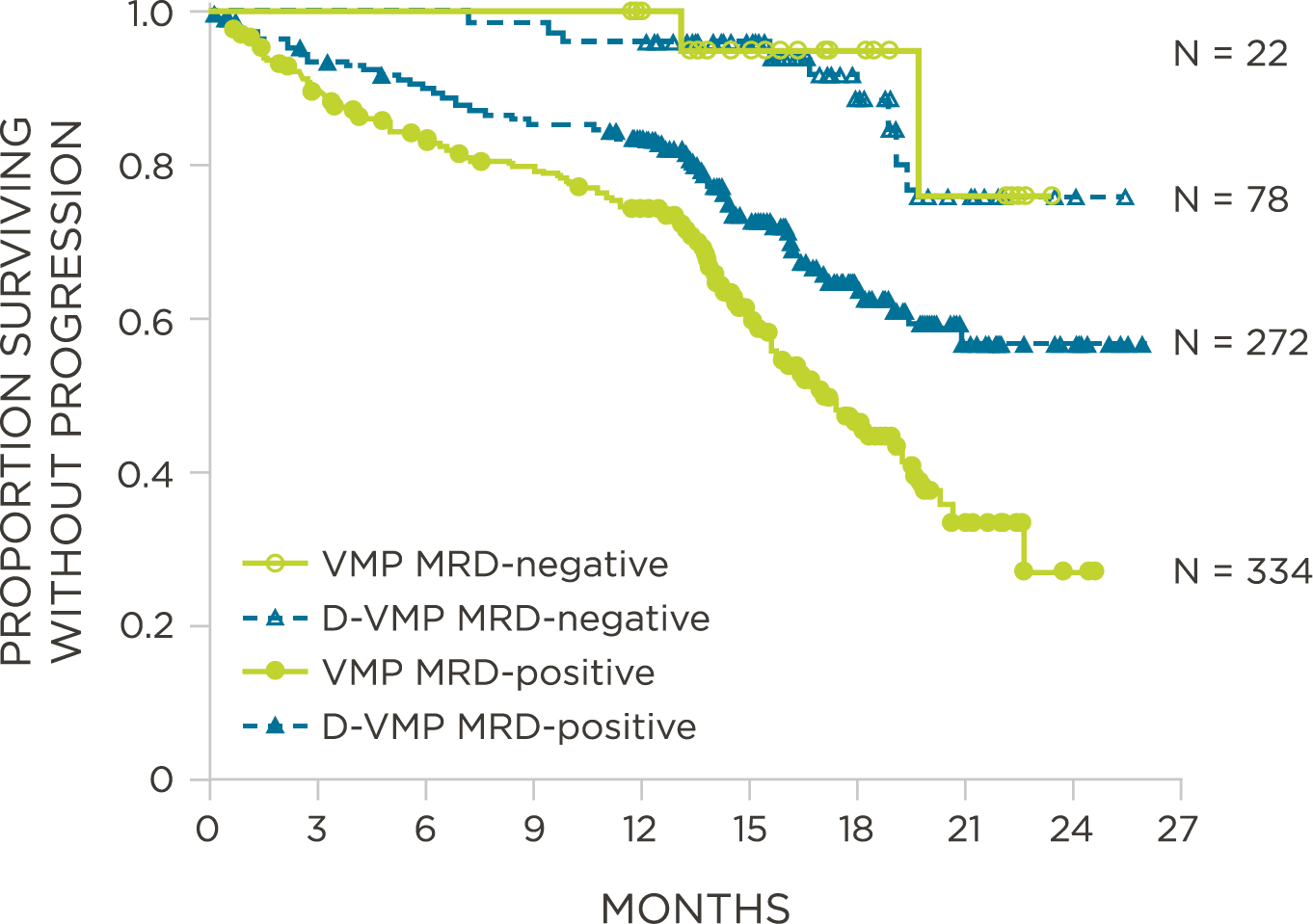
Peer-reviewed publications show advantages to using clonoSEQ in Multiple Myeloma:
MRD assessment by clonoSEQ predicts time to tumor progression (TTP) and overall survival (OS).[8]
View More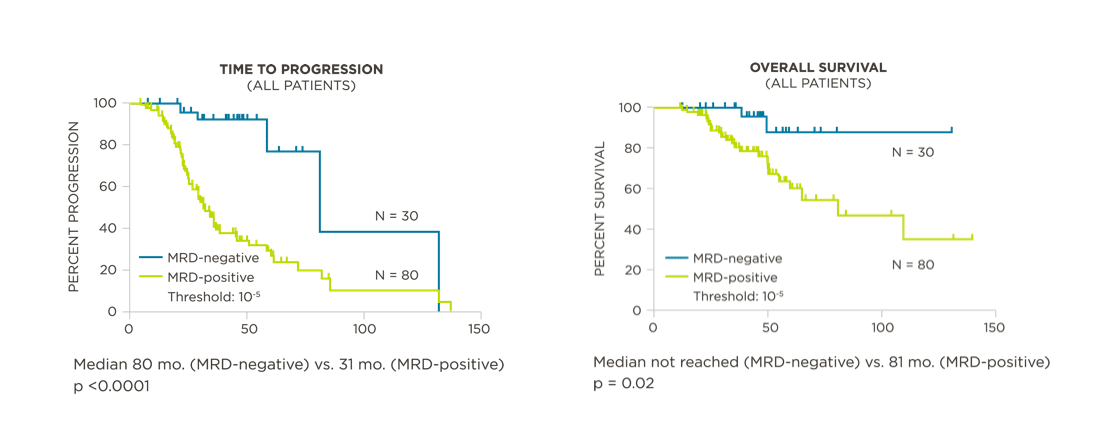
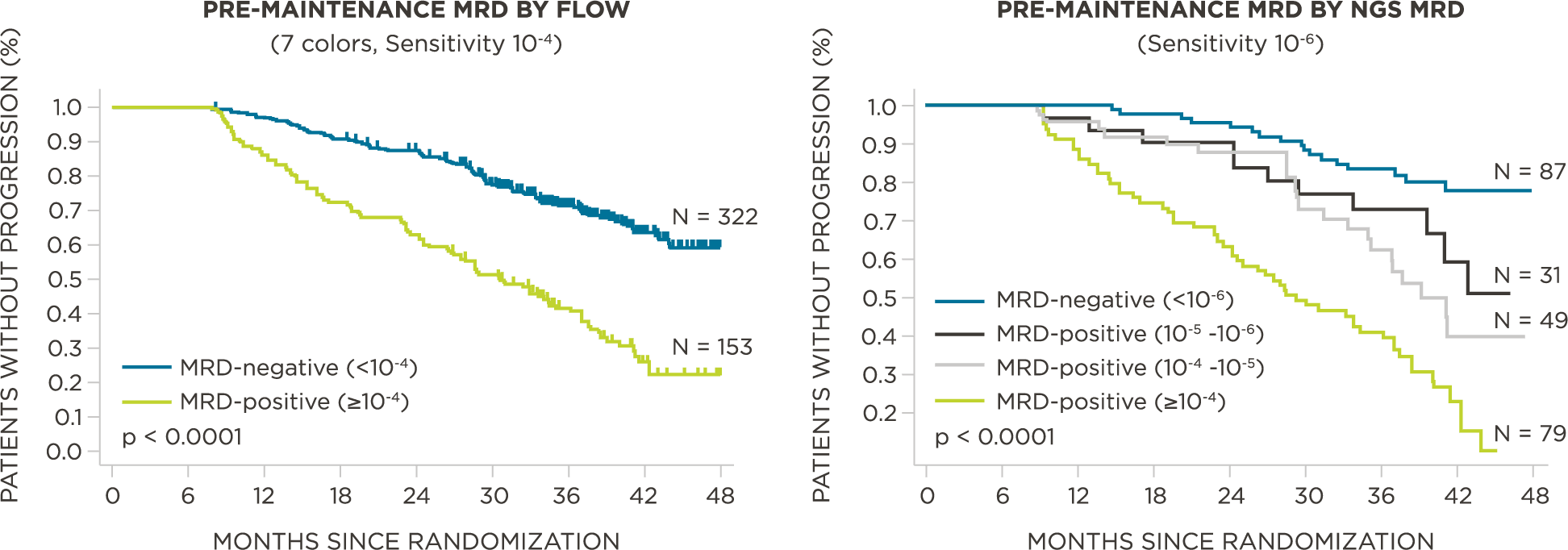
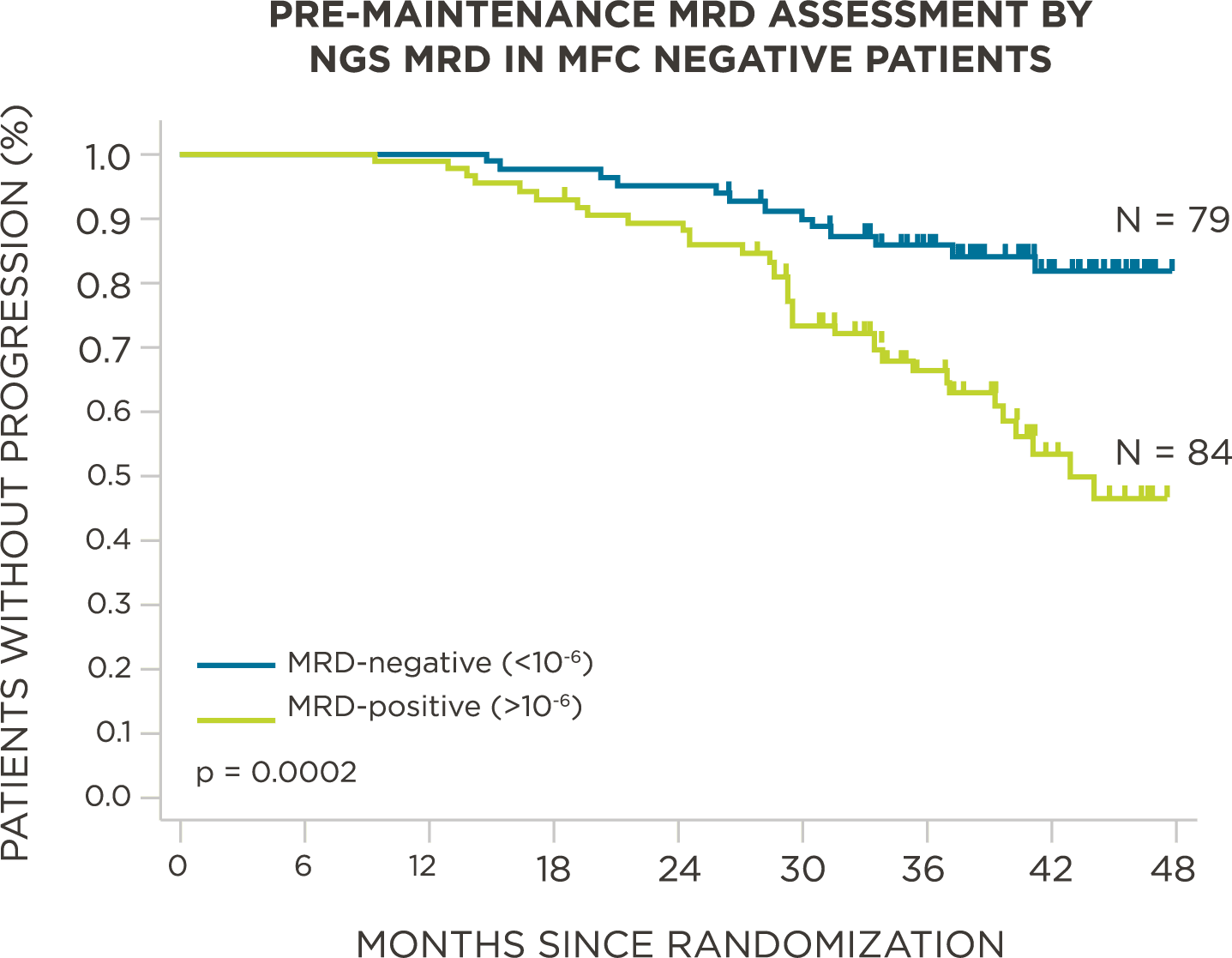
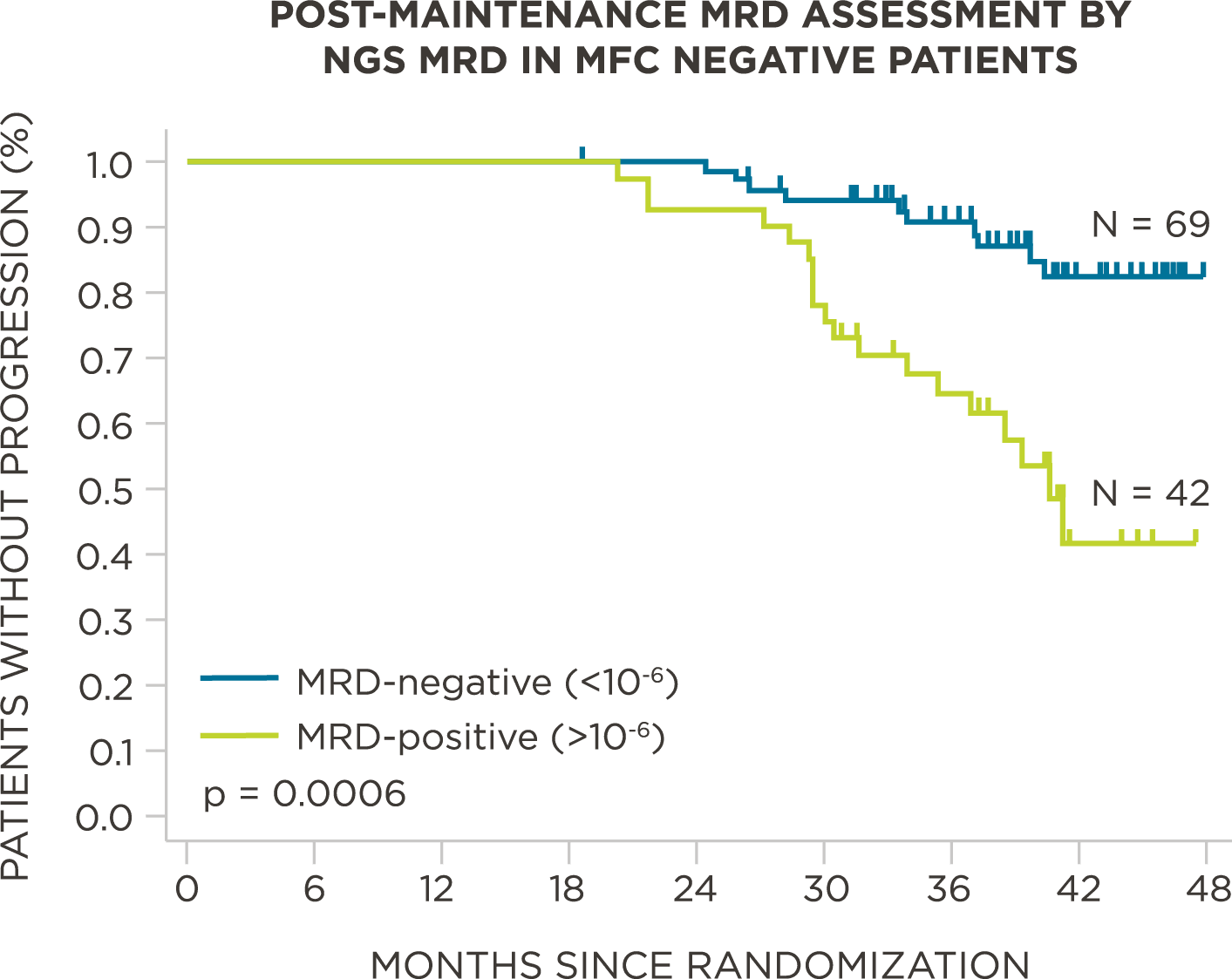
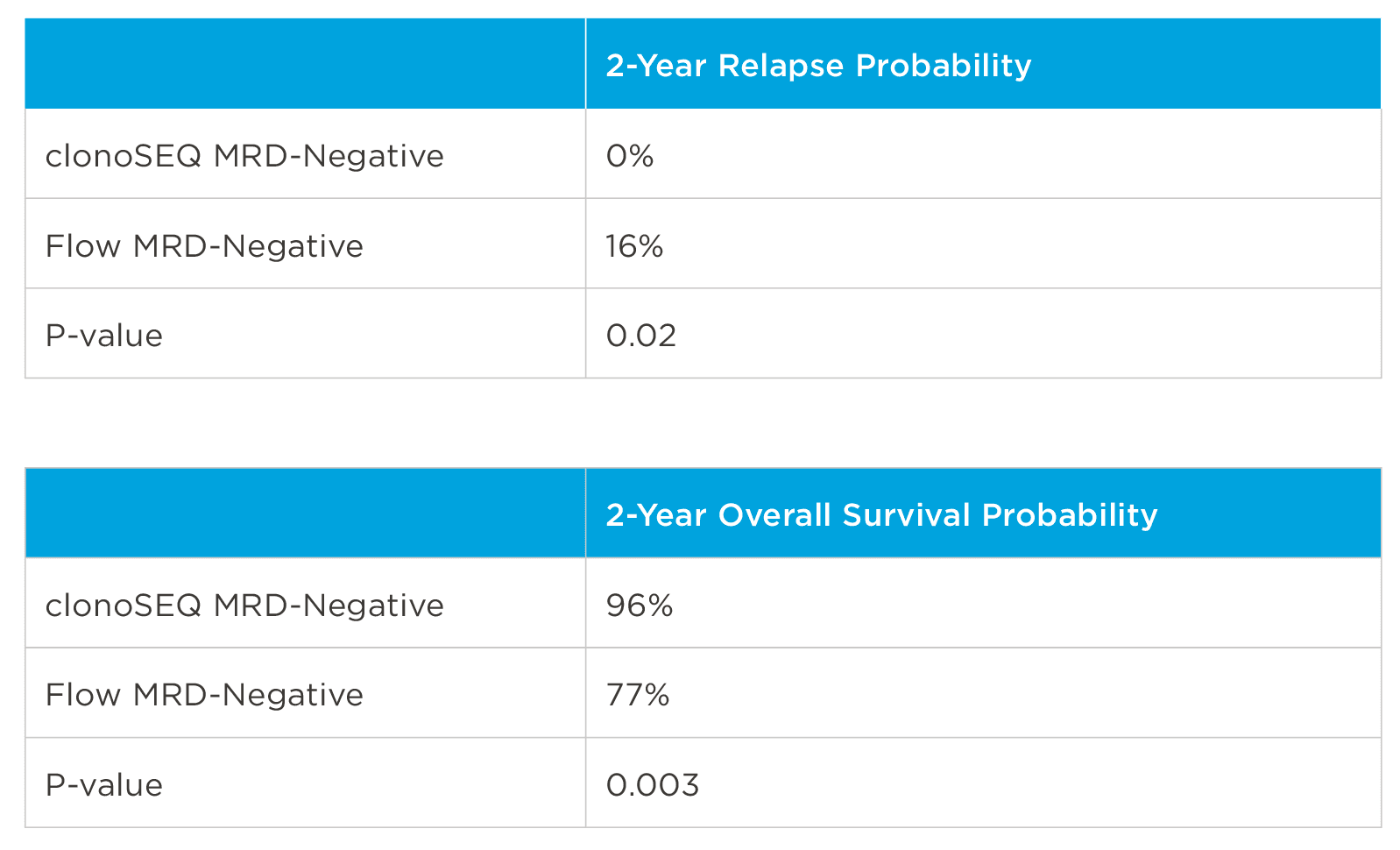
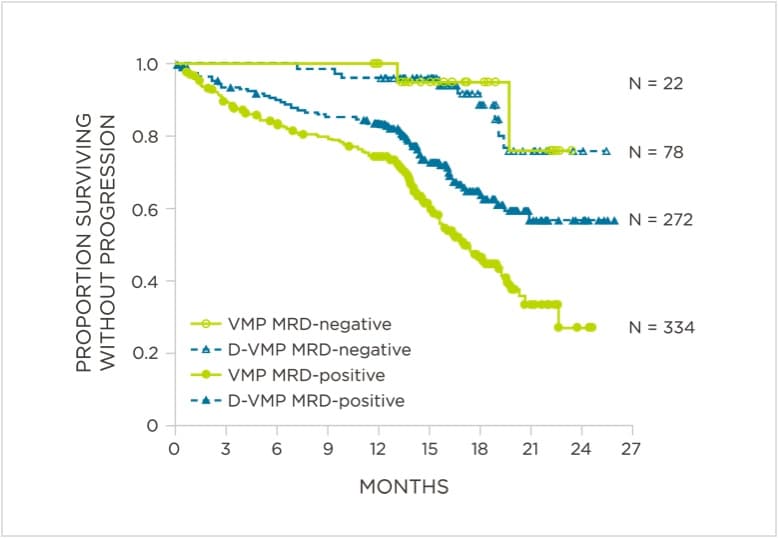
MRD negativity when assessed pre- and post-maintenance at deeper sensitivity correlated with improved outcomes.
View More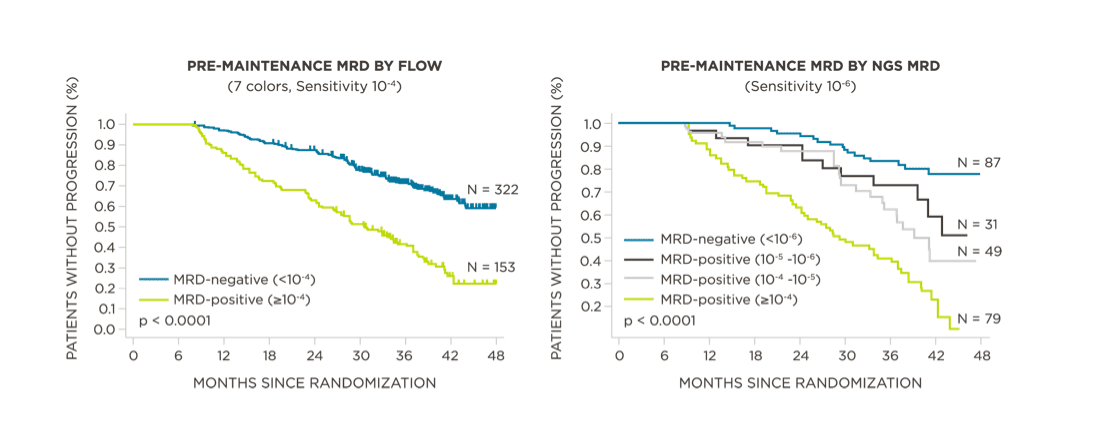
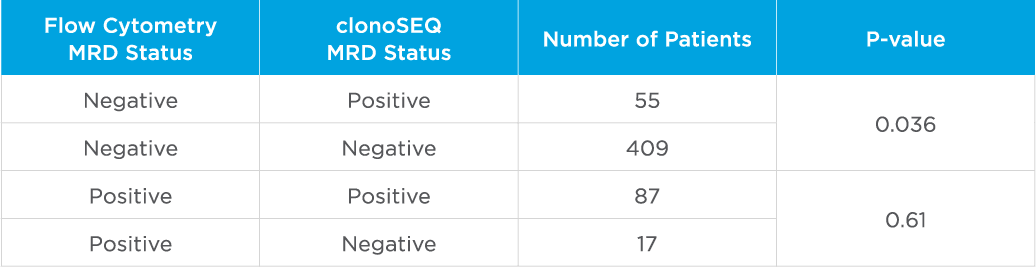
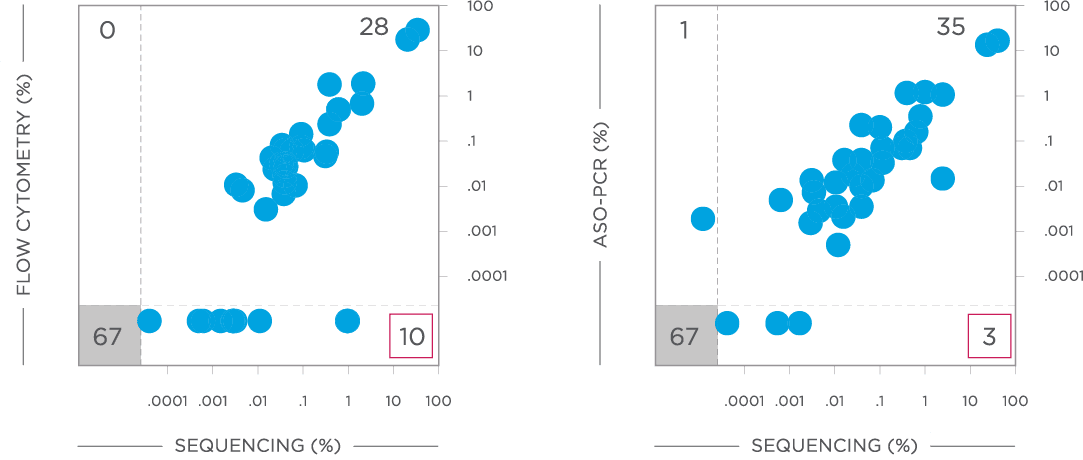
clonoSEQ MRD testing identified additional MRD-positive patients who were MRD-negative by flow cytometry in this study.
View More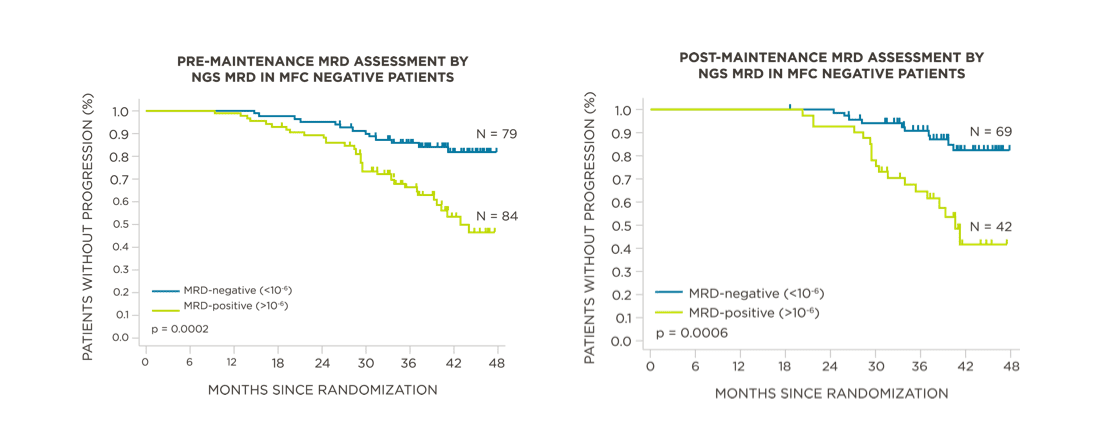
Download Myeloma Clinical Data
Download our Multiple Myeloma clinical data summary to explore and share the data.
VIEW PDFReview NCCN Guidelines®
Access the NCCN Guidelines.
GUIDELINESAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Data Spotlight
PATIENT POPULATION:
579 pediatric patients were assessed for MRD at baseline and end of induction (Day 29)
STUDY OBJECTIVE:
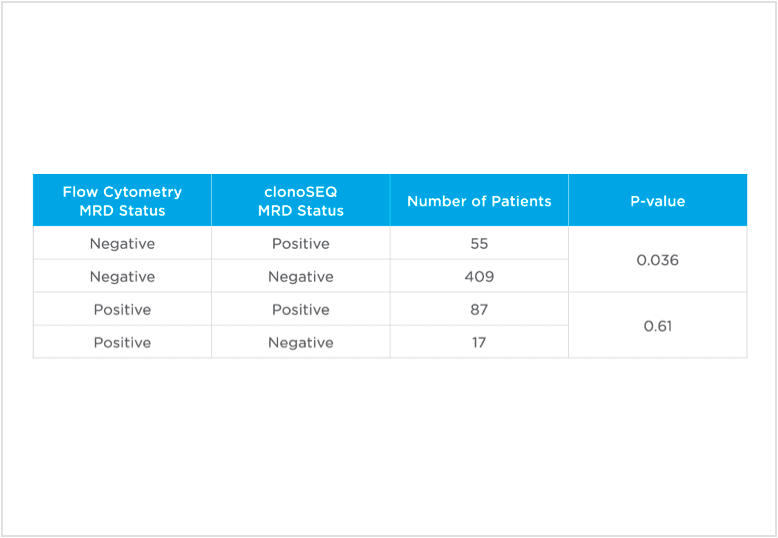
Evaluate non-inferiority of clonoSEQ to flow cytometry using an MRD threshold of 10-4 and understand if increased sensitivity of clonoSEQ identifies additional patients with residual disease compared to flow cytometry. Assessment of MRD at end of induction showed that sequencing-based MRD detection identified an additional 55 patients who were MRD-positive by the clonoSEQ Assay and MRD-negative by flow cytometry (p=0.036).[3]
Peer-reviewed publications show advantages to using clonoSEQ in ALL:
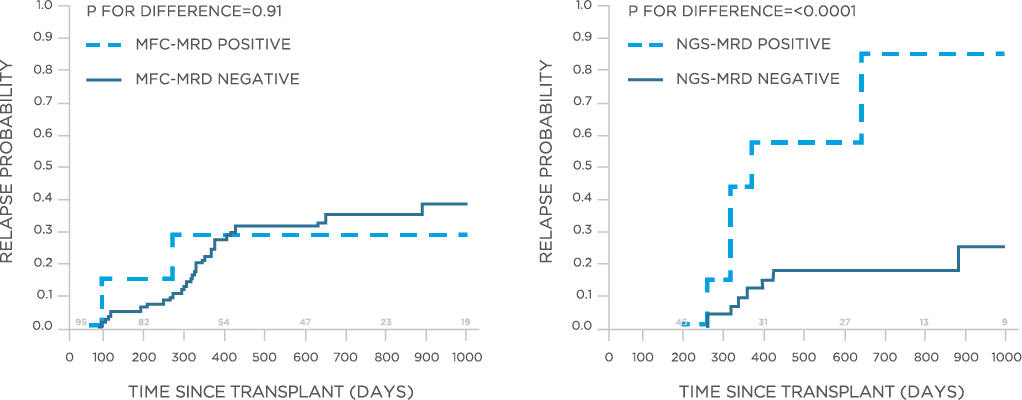
In one study, clonoSEQ was shown to be superior to flow cytometry in predicting post treatment relapse and survival.[13]
View More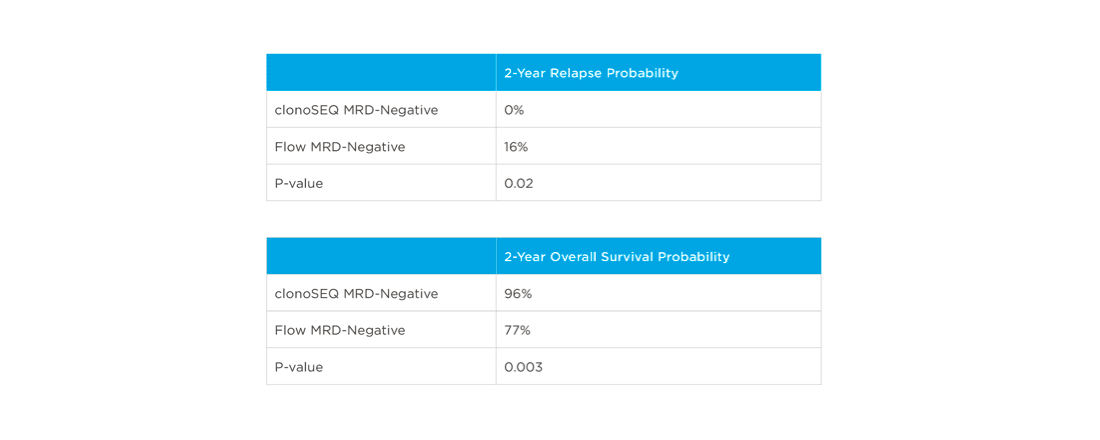
clonoSEQ may be used to predict relapse and disease free survival in the post-transplant setting.[13]
View More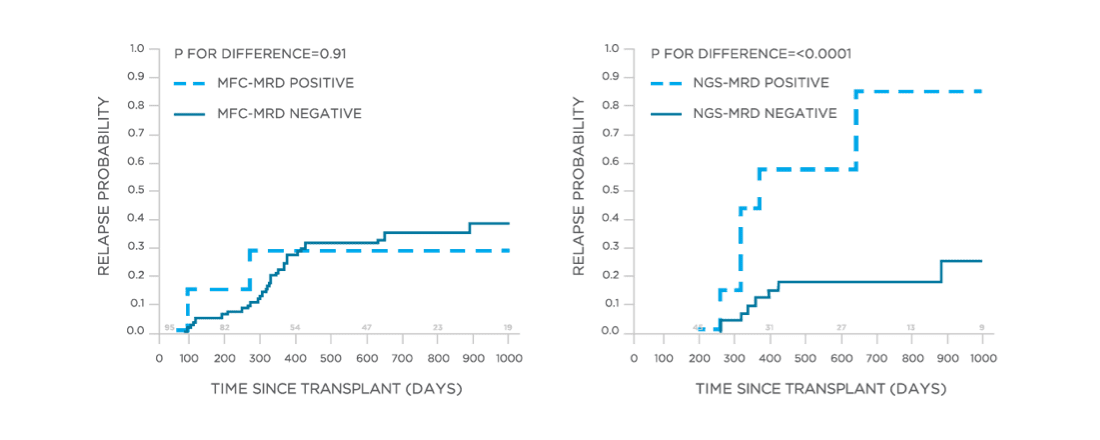
clonoSEQ is concordant with traditional methods for MRD detection and offers increased sensitivity.[12]
View More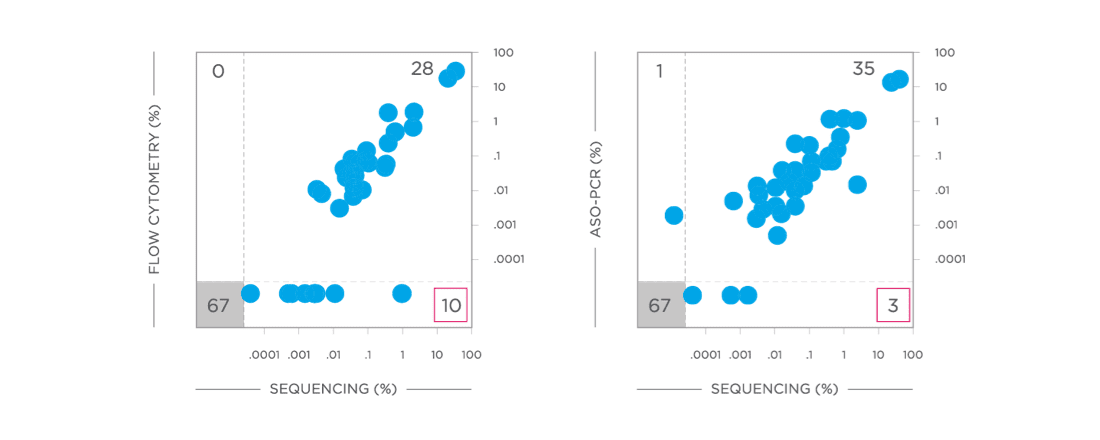
Download ALL Clinical Data
Download our Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia clinical data summary to explore and share the data.
VIEW PDFReview NCCN Guidelines®
Access the NCCN Guidelines.
GUIDELINESClinical studies show advantages to using clonoSEQ in CLL:
clonoSEQ predicts outcomes in both bone marrow and peripheral blood samples.
View More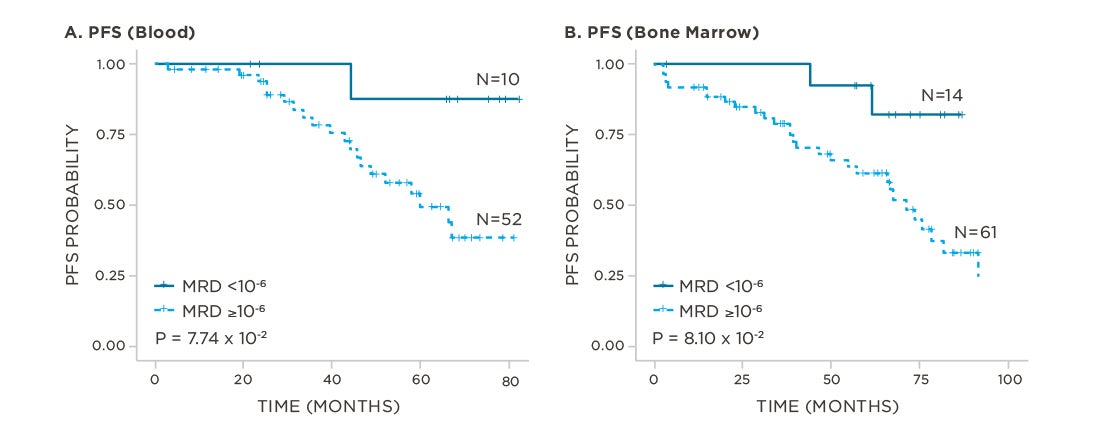
This page is intended for use by healthcare professionals outside of the United States.
The clonoSEQ Assay B-cell Reagent Set is an in vitro diagnostic that identifies and quantifies rearranged B-cell receptor gene sequences in DNA extracted from blood and bone marrow.
It is a manual test that determines measurable/minimal residual disease (MRD) and monitors changes in disease burden during and after treatment in B-cell malignancies. The test is indicated for use by qualified healthcare professionals for clinical decision-making and in conjunction with other clinicopathological features.
The clonoSEQ Assay is being utilized for a variety of investigator-sponsored clinical trials in B-cell lymphoid cancers. If you are interested in learning more about use of clonoSEQ in your own trials, contact dxsupport@adaptivebiotech.com.
Download CLL Clinical Data
Download our Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia clinical data summary to explore and share the data.
VIEW PDFReview NCCN Guidelines®
Access the NCCN Guidelines.
GUIDELINESMedical Affairs inquiries
Make an inquiry to learn more about our products.
Citations
- clonoSEQ®. [technical summary]. Seattle, WA: Adaptive Biotechnologies; 2020. https://clonoseq.com/technical-summary.
- Perrot A, et al. Blood. 2018;132(23):2456-2464.
- Wood B, et al. Blood. 2018;131(12):1350-1359.
- Kumar S, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(8):e328-e346.
- Mateos M, et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(6):518-528.
- DARZALEX® Prescribing Information. Horsham, PA: Janssen Biotech, Inc; 2018.
- Dimopoulos M, et al. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(14):1319-31.
- Martinez-Lopez J, et al. Blood. 2014;123(20):3073-3079.
- Avet Loiseau H, et al. ASH 2015: Abstract 191.
- Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Multiple Myeloma V.3.2020. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2020. All rights reserved. Accessed March 11th, 2020. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go to NCCN.org.
- Moreau P, et al. Ann Oncol. 2017;00:1-11.
- Faham M, et al. Blood. 2012;120(26):5173-5180. (study author was an employee of Adaptive at time of publishing)
- Pulsipher M, et al. Blood. 2015;125(22):3501-8.
- Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia V.2.2020. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2020. All rights reserved. Accessed March 11th, 2020. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go to NCCN.org.
- Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia V.1.2020. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2020. All rights reserved. Accessed March 11th, 2020. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go to NCCN.org.
- Hoelzer D, et al. Ann Oncol. 2016;27 (suppl_5): v69-v82.
- Thompson P, et al. Blood. 201928;134(22):1951-1959.
- Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Leukemia V.4.2020. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2020. All rights reserved. Accessed [February 19, 2020]. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go online to NCCN.org.